Understanding and Managing Chiggers in Your Bedroom


Intro
Chiggers, also known as harvest mites, often create unease when they invade spaces where we expect safety. These tiny parasitic larvae are widely misunderstood and often confused with other pests. Understanding their biology and behavior is essential for effective management in the household, particularly in the bedroom where comfort should be a priority. This guide will unveil the key aspects of chigger management, ranging from identification to eco-friendly pest control options.
Identification of Common Pests
Description of Common Pests
Chiggers are not insects but rather the larval form of the Trombiculidae family. They are extremely small, typically measuring about 0.2 to 0.3 mm, and cannot be seen without magnification. Their reddish-orange color, however, can be a distinguishing feature. Unlike some pests, they do not burrow into the skin but instead latch onto hosts to feed by injecting digestive enzymes that break down skin cells. This feeding occurs primarily in the warmer months, making it crucial to be vigilant during this period.
Signs of Infestation
Identifying chigger infestations can be tricky due to their size. However, here are some indications:
- Red, itchy welts: These typically appear after prolonged contact with infested areas.
- Presence of chiggers in bedding: A careful inspection may reveal their presence on sheets or pillowcases.
- Localized irritation: Noticeable reactions may emerge on skin areas covered by bedding after a night’s sleep.
It’s important to track these symptoms and act promptly to minimize discomfort.
Prevention Techniques
Home Maintenance Tips
Routine maintenance plays a significant role in managing chiggers in living spaces. Here are applicable steps to consider:
- Regularly wash bedding: Using hot water can help eliminate any chiggers that may have found their way into the fabric.
- Vacuum frequently: This step helps to remove not only chiggers but also potential hosts such as fleas that can contribute to infestations.
- Seal cracks and crevices: Ensure windows and doors are properly sealed to avoid outdoor pests from entering.
Environmental Modifications
Chiggers thrive in certain environments. Modifications can help deter them:
- Keep grass and weeds trimmed: This limits the areas where chiggers can thrive outdoors.
- Create barriers: Using landscaping techniques can make it difficult for chiggers to access the home.
- Limit pets’ access to infested areas: Pets can bring chiggers indoors, so be cautious about their roaming habits.
Eco-Friendly Pest Control Options
Natural Pesticides
For those conscious of chemicals, natural pesticides can be effective alternatives. Some examples include:
- Diatomaceous earth: This abrasive substance can help eliminate chiggers by damaging their exoskeletons.
- Essential oils: Certain oils like tea tree or peppermint act as natural repellents against various pests, including chiggers.
Organic Pest Control Techniques
Implementing organic methods can also support chigger management:
- Beneficial insects: Introducing pest-eating insects can help control chigger populations.
- Homemade sprays: Combining water with vinegar and essential oils can enhance preventative measures.
Staying informed about chiggers and their management is crucial for maintaining a comfortable living environment. By understanding their behavior and implementing these strategies, homeowners can effectively safeguard their bedrooms and enjoy a more peaceful rest.


Prelims to Chiggers
Chiggers are tiny, red larvae often overlooked yet capable of causing significant discomfort. Understanding chiggers is essential for homeowners. Their presence can disrupt a peaceful living environment, particularly in bedrooms where individuals expect to rest undisturbed. Recognizing the characteristics and behavior of chiggers provides the foundation for effective management and prevention strategies.
The potential impact of chiggers extends beyond minor skin irritation. They may lead to more extensive infestations in your home, making awareness even more critical. By grasping their biology and life cycle, one can identify conditions conducive to their presence. Furthermore, understanding geographical distribution helps you gauge the risk of encountering these pests in various regions, thereby enabling appropriate preparations.
Chiggers in the Bedroom
This section will discuss what chiggers are, their biological traits, and where they are commonly found. By acquiring this knowledge, homeowners can take proactive steps towards mitigating risks posed by chiggers in their living spaces.
Chiggers in the Household
Understanding chiggers in your home is crucial, especially when it comes to maintaining a comfortable and healthy living environment. These small pests are often overlooked due to their size, yet their presence can be a nuisance and can lead to uncomfortable bites. Among the various areas in a household, the bedroom often presents unique challenges when it comes to controlling chiggers. This section explores different aspects that homeowners should consider to manage these pests effectively.
Potential Entry Points
Chiggers can infiltrate homes through various entry points. Understanding these paths helps in preventing their movement indoors. Here are some key areas to monitor:
- Windows and Doors: Gaps in screen windows or improperly sealed doors allow chiggers to enter. Regularly inspect screens and ensure doors are closed tightly.
- Openings and Cracks: Examine the foundation and walls for any cracks. Chiggers can find their way through these unnoticed openings.
- Pet Fur: Pets often bring chiggers indoors. Regular grooming and bathing can reduce this risk.
- Outdoor Clothing: If you spend time in grassy or wooded areas, chiggers can cling to your clothes. Remove outdoor garments upon returning home and wash them promptly.
By recognizing these potential entry points, you can take effective steps to minimize the risk of chigger infestations in your home.
Understanding Their Behavior
Knowing the behavior of chiggers can inform better management approaches. Chiggers are most active during hot and humid conditions, usually thriving in gardens, fields, and forests. They tend to feed primarily on the skin of warm-blooded animals, including humans.
Chiggers do not burrow into the skin, as many believe. Instead, they inject saliva that liquefies skin cells, which they then consume. This feeding process results in the infamous itchy bites that most people associate chiggers with. To mitigate their impact, try to limit outdoor activities in areas where chiggers are prevalent, especially during peak times of their activity.
Chiggers in Bedding: Myths vs. Facts
There are several misconceptions about chiggers and their presence in bedding, which can contribute to unnecessary panic. Here are a few clarifications:
- Myth: Chiggers live in mattresses.
- Myth: Chigger bites come from chiggers being in your bed.
- Myth: Chiggers can cause long-term skin damage.
- Fact: Chiggers do not reside in bedding. They are primarily outdoor pests.
- Fact: Bites usually occur when people wander through infested areas and inadvertently bring chiggers into their homes. Thus, ensuring clean clothes and body after exposure is vital.
- Fact: Chigger bites, while irritating, usually heal on their own without lasting effects.
Understanding these myths helps reduce fear and promotes practical preventative measures. Regular cleaning and proper clothing management strategies are your best defense against these small pests.
Identifying Chigger Bites
Identifying chigger bites is critical for effective management of infestations. Recognizing the signs early can significantly reduce discomfort and mitigate the risk of confusion with bites from other pests. Misidentifying chigger bites can lead to improper treatments, prolonging the discomfort. By knowing the unique characteristics of these bites, homeowners can take the necessary steps to manage their environment more effectively.
Symptoms of Chigger Bites
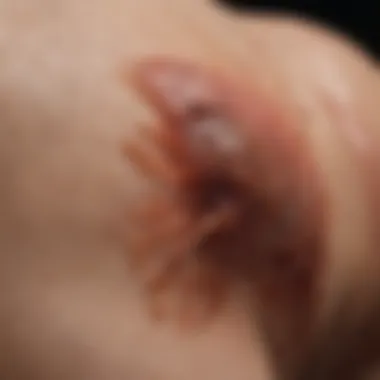

Chigger bites typically manifest as small red welts on the skin. Initially, these may look similar to regular insect bites, but distinctive features set them apart. The bites usually become itchy within a few hours. This itching can worsen, leading to more significant irritation and scratching, which may result in secondary infections. Common symptoms include:
- Red, raised welts: Often appearing in clusters.
- Intense itching: The most notable symptom, which can disrupt sleep.
- Swelling and inflammation: The area around the bites may feel warm and tender.
- Location: Chiggers tend to bite areas where skin is thin, like around waistbands, underarms, and behind the knees.
Differentiating from Other Insect Bites
It is essential to distinguish chigger bites from those of other insects. This differentiation aids in determining the appropriate treatment and prevention strategies. Several factors help in identifying chigger bites:
- Timing of Symptoms: Chigger bites become bothersome hours after exposure, often peaking in irritation within 24 hours.
- Appearance: Unlike mosquito bites, which are usually solitary and fluid-filled, chigger bites appear clustered and can feel like raised bumps.
- Location: Many bites from other insects are more random; however, chigger bites are common in areas of skin constriction, such as where clothing fits tightly.
Recognizing the unique patterns of chigger bites is vital. Misidentifying can lead to ineffective treatments.
Preventing Chigger Infestations
Preventing chigger infestations is crucial not only for maintaining a comfortable living environment but also for protecting the health of those who reside in the home. Chiggers, though microscopic, can cause significant discomfort through their bites. Therefore, implementing effective prevention strategies can mitigate the risks associated with these pests and promote a healthier indoor space.
Cleaning and Maintenance Strategies
Maintaining a clean household is one of the most effective ways to prevent chigger infestations. Regular cleaning helps eliminate potential habitats where chiggers might thrive. Here are some essential practices to consider:
- Vacuuming: Regularly vacuum carpets, rugs, and upholstery. Be sure to focus on areas that might trap debris, such as corners and under furniture. This removes chiggers, dead skin, and other debris that can attract them.
- Washing Bedding: Wash all bedding materials—sheets, pillowcases, and blankets—in hot water regularly. This process not only kills chiggers but also removes any eggs that may be present.
- Decluttering: Minimize clutter in the bedroom and around the house. Chiggers can find refuge in piles of clothes or other forgotten items. Keeping spaces organized makes it harder for them to establish a presence.
By incorporating these cleaning protocols into your routine, you create an inhospitable environment for chiggers and significantly lower the risk of infestation.
Using Barriers and Protective Measures
Implementing barriers and protective measures is another effective strategy in preventing chigger populations from establishing themselves in your home. Using physical barriers reduces the chances of these pests invading your space. Consider the following:
- Sealing Cracks and Gaps: Inspect your home for cracks in walls, gaps in windows, or spaces around doors. Seal any openings using caulk or weather-stripping. This prevents chiggers from entering your living quarters from outside.
- Installing Screens: Use fine mesh screens for windows and vents. This simple measure allows airflow while keeping pests at bay.
- Encasing Mattresses: Protect your bedding by using encasement covers designed for mattresses and pillows. These covers deter chiggers and other pests from making your bed their home.
These barriers not only provide a defense against chiggers but also improve the overall integrity of your home.
Repellents: What Works?
The use of repellents can be an effective way to reduce the risk of chigger infestations. Various products can provide an additional layer of protection. Here are some useful options:
- Permethrin: This is an insect repellent specifically formulated for use on clothing and gear. It can effectively kill chiggers upon contact. Apply it to all outdoor clothing and let it dry before wearing.
- DEET-Based Sprays: DEET is a well-known repellent effective against various insects, including chiggers. Apply on skin, especially when spending time outdoors. However, follow application instructions for safety.
- Essential Oils: Some natural repellents using essential oils such as lavender or eucalyptus can deter chiggers. While not as effective as synthetic options, they serve as a gentle alternative for those preferring naturals.
Effective Treatment Options
When dealing with chigger infestations, understanding the available treatment options is essential. Treatments can minimize discomfort from bites and tackle the underlying issue of chigger presence in the household. Choosing an appropriate strategy involves recognizing specific needs based on severity, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility.
In the following subsections, we will delve into various solutions for managing chigger issues. It is vital to keep in mind that the effectiveness of each method can vary. Individual circumstances will shape the best fit for a household.
Home Remedies
Many homeowners turn to home remedies when dealing with chigger bites. These treatments often involve using common household items and may be effective in alleviating symptoms.


- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress can help reduce itching and swelling. Use a cloth soaked in cold water or an ice pack wrapped in a towel for about 10 to 15 minutes.
- Baking Soda: This common pantry item can reduce itching. Make a paste with water and apply it to the affected area for temporary relief.
- Oatmeal Bath: An oatmeal bath is another soothing option. Colloidal oatmeal, which can be found in many grocery stores, may help calm irritated skin.
- Aloe Vera: This plant is known for its soothing properties. Applying fresh aloe vera gel can alleviate irritation and promote healing.
While these remedies may provide relief, results can vary. If symptoms worsen or persist, other treatments might be necessary.
Over-the-Counter Solutions
Over-the-counter (OTC) treatments are widely available and can offer more targeted relief for chigger bites. Here are some common options:
- Antihistamines: These can help with itching and reduce allergic reactions. Medications such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can be taken orally but be aware of drowsiness as a side effect.
- Hydrocortisone Cream: This cream can reduce inflammation and itching. Apply as directed on the label, but avoid overuse, since long-term use may thin the skin.
- Calamine Lotion: Known for its soothing effects, calamine lotion can relieve itching and promote healing.
When using OTC treatments, it is advisable to follow the instructions on the packaging carefully. Most of these products are effective for mild cases and can alleviate discomfort.
When to Seek Professional Help
In certain situations, it may be necessary to consult a healthcare professional. Pay attention to the following warning signs:
- Severe Reactions: If you experience swelling, difficulty breathing, or other severe symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
- Infection Signs: Redness, warmth, or pus around the bite site may indicate infection. This requires prompt treatment from a healthcare provider.
- Persistent Symptoms: If the itching, swelling, or discomfort does not improve after several days of using home or OTC remedies, you should consult a doctor.
- Underlying Health Conditions: People with certain health issues or weakened immune systems may require a tailored approach. Consulting a doctor in such cases is sensible.
In summary, understanding the array of treatment options can empower homeowners to make informed choices. Each method has its benefits, but appropriate use is key to effective relief from chigger bites.
Long-Term Control Measures
Addressing chigger infestations requires a holistic view that integrates long-term control measures. These strategies are not merely reactive, but rather proactive approaches that ensure your household remains free from these pests over time. A sustained effort will mitigate the risk of re-infestation, enhancing the comfort and safety of your living environment.
Integrating Pest Management Strategies
Pest management is a systematic approach which combines various techniques to ensure long-term control of chigger populations. This includes environmental management, regular cleaning, and possibly the use of professional pest control services. Consider the following elements:
- Environmental Management: Modify the habitat around your home. Reducing dense vegetation and maintaining a tidy garden can limit chigger habitats.
- Regular Cleaning: Frequent vacuuming and dusting can eliminate potential egg and larva deposits. Use a vacuum with a fine filter to ensure thorough cleaning, particularly in bedrooms, where chiggers may hide.
- Community Awareness: Engaging neighbors in collective pest management efforts can yield better results. Chiggers do not recognize property lines, thus a united front can impede their movement from one area to another.
Integrating these strategies is not only cost-effective but also reinforces a culture of cleanliness and vigilance within a household.
Monitoring for Future Infestations
Continuous monitoring is vital in the fight against chiggers. Regular inspections can help identify any signs of re-infestation early. Consider these monitoring tactics:
- Routine Inspections: Schedule periodic checks of bedding and carpets. Early symptoms of a chigger presence include itchy dots or persistent bites, which can indicate a need for immediate action.
- Tracking Seasonal Patterns: Chigger activity typically increases during warmer months. Anticipating these patterns can help homeowners stay ahead of potential infestations. When the season approaches, increase your cleaning frequency to keep chiggers at bay.
- Setting Up Traps: Utilizing chigger traps in vulnerable areas can provide insight into their population density. This proactive measure offers data to inform your management strategies.
"Proactive measures and continuous monitoring form the cornerstone of an effective long-term control plan against chiggers."
By employing these methods, homeowners can enhance their living environment's overall health and comfort, minimizing the risks associated with chigger infestations.
Culmination
Recap of Key Points
In summary, the key points discussed throughout the article include:
- Nature of Chiggers: Chiggers are tiny mites that can cause itchy bites, primarily found in grassy areas but can invade homes.
- Identifying Bites: The symptoms of chigger bites should not be mistaken for other insect bites. It's essential to understand what to look for to ensure accurate identification.
- Prevention Techniques: Regular cleaning, appropriate use of barriers, and specific repellents can significantly reduce the chances of chigger infestations.
- Treatment Options: Both home remedies and over-the-counter solutions can effectively manage chigger bites and provide relief.
- Long-Term Control: Implementing pest management strategies is necessary for dealing with chigger issues over time and monitoring for possible re-infestations.
Final Thoughts on Managing Chiggers
Managing chiggers requires understanding their behavior and lifecycle. Homeowners should actively adopt cleaning and preventive practices regularly. By being proactive, any potential discomfort caused by chiggers can be minimized.
It is advisable to regularly check bedding and frequently wash linens to thwart any infestations. Additionally, utilizing effective treatment options for bites can help in managing discomfort. Comprehensive knowledge about managing chiggers leads to fewer disruptions in daily life and improved living conditions overall. Ultimately, addressing these tiny pests in a meticulous manner can contribute to a more enjoyable home environment, free of unnecessary worry about irritating bites.







